Todays pic is a view of a moon of a backyard neighbour in terms of distance when considered in the sense of astronomy.
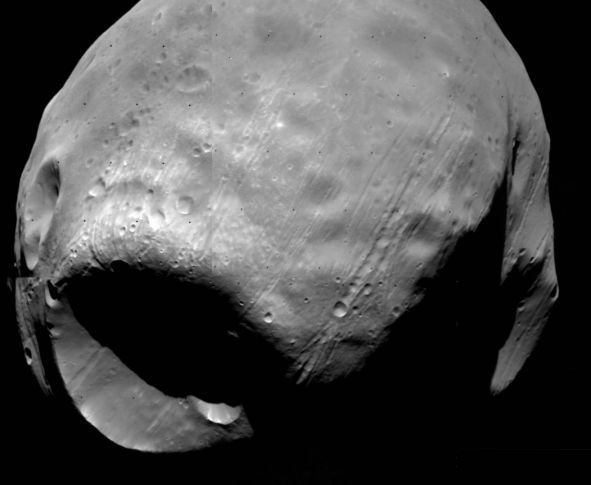
Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
This moon is doomed. Mars, the red planet named for the Roman god of war, has two tiny moons, Phobos and Deimos, whose names are derived from the Greek for Fear and Panic. These Martian moons may well be captured asteroids originating in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter or perhaps from even more distant reaches of the Solar System. In this 1978 Viking 1 orbiter image, the largest moon, Phobos, is indeed seen to be a heavily cratered asteroid-like object. About 17 miles across, Phobos really zips through the Martian sky. Actually rising above Mars' western horizon and setting in the east, it completes an orbit in less than 8 hours. But Phobos orbits so close to Mars, (about 5,800 kilometers above the surface compared to 400,000 kilometers for our Moon) that gravitational tidal forces are dragging it down. In 100 million years or so it will likely crash into the surface or be shattered by stress caused by the relentless tidal forces, the debris forming a ring around Mars.
Credit: Viking Project, JPL, NASA; Image mosaic by Edwin V. Bell II (NSSDC/Raytheon ITSS)
A larger version of this pic can be found here, this is a 74K Jpeg image.
Previous Pic Of The Day posts
03rd Apr 03
30th Mar 03
28th Mar 03
26th Mar 03
22nd Mar 03
21st Mar 03
20th Mar 03

Phobos: Doomed Moon of Mars
This moon is doomed. Mars, the red planet named for the Roman god of war, has two tiny moons, Phobos and Deimos, whose names are derived from the Greek for Fear and Panic. These Martian moons may well be captured asteroids originating in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter or perhaps from even more distant reaches of the Solar System. In this 1978 Viking 1 orbiter image, the largest moon, Phobos, is indeed seen to be a heavily cratered asteroid-like object. About 17 miles across, Phobos really zips through the Martian sky. Actually rising above Mars' western horizon and setting in the east, it completes an orbit in less than 8 hours. But Phobos orbits so close to Mars, (about 5,800 kilometers above the surface compared to 400,000 kilometers for our Moon) that gravitational tidal forces are dragging it down. In 100 million years or so it will likely crash into the surface or be shattered by stress caused by the relentless tidal forces, the debris forming a ring around Mars.
Credit: Viking Project, JPL, NASA; Image mosaic by Edwin V. Bell II (NSSDC/Raytheon ITSS)
A larger version of this pic can be found here, this is a 74K Jpeg image.
Previous Pic Of The Day posts
03rd Apr 03
30th Mar 03
28th Mar 03
26th Mar 03
22nd Mar 03
21st Mar 03
20th Mar 03





