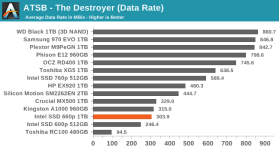
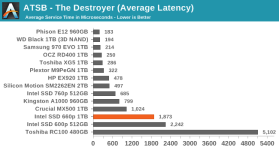
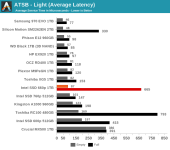
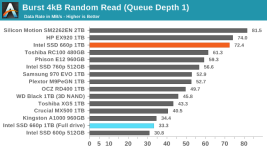
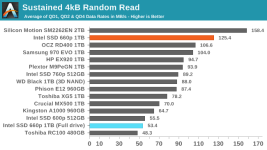
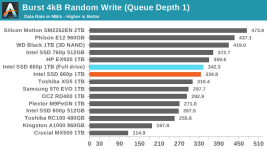
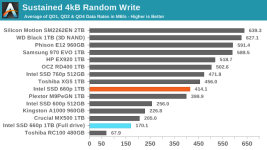
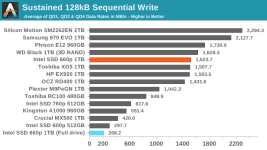
Even though our synthetic tests are designed to give drives a reasonable amount of idle time to flush their SLC write caches, the 660p keeps most of the data as SLC until the capacity of QLC becomes necessary. This means that when the SLC cache does eventually fill up, there's a large backlog of work to be done migrating data in to QLC blocks. We haven't yet quantified how quickly the 660p can fold the data from the SLC cache into QLC during idle times, but it clearly isn't enough to keep pace with our current test configurations. It also appears that most or all of the tests that were run after filling the drive up to 100% did not give the 660p enough idle time after the fill operation to complete its background cleanup work, so even some of the read performance measurements for the full-drive test runs suffer the consequences of filling up the SLC write cache.
In the real world, it is very rare for a consumer drive to need to accept tens or hundreds of GB of writes without interruption. Even the installation of a very large video game can mostly fit within the SLC cache of the 1TB 660p when the drive is not too full, and the steady-state write performance is pretty close to the highest rate data can be streamed into a computer over gigabit Ethernet. When copying huge amounts of data off of another SSD or sufficiently fast hard drive(s) it is possible to approach the worst-case performance our benchmarks have revealed, but those kind of jobs already last long enough that the user will take a coffee break while waiting.




 I dont mind spending a bit more and getting something better.
I dont mind spending a bit more and getting something better.
 I've seen a 2TB 660p for £190 today, so zen's release time will be great.
I've seen a 2TB 660p for £190 today, so zen's release time will be great.